Processing explains mass, charge, and why neutrinos exist, but what about anti-matter? Dirac’s equations predicted anti-matter before it was found, but why do all matter particles have evil twins of the same mass but opposite charge? The standard model just added an anti-matter column to fit the facts, but why matter has an inverse is a mystery, as how can a substance have an anti-substance?
However if matter arises from a process, the same process in reverse can produce antimatter. Processing predicts anti-processing, as a process can run both ways, so matter must allow anti-matter.
So far, we have taken the basic network process to be a clockwise circle, but an anti-clockwise circle would work just as well. For light, a clockwise process means that photons go first up then down on the surface of space, while for an anti-clockwise process they go first down then up. These two photon types, first-up and first-down, aren’t equivalent.
What would a universe based on an anti-clockwise process be like? For an electron, it would produce the same net processing but a positive remainder, so an anti-electron has the same mass as an electron but a positive charge. Anti-processing not only explains anti-electrons, but also why they annihilate any electrons they meet. Anti-matter then is to matter as neutrinos are to electrons, a necessary alternative.
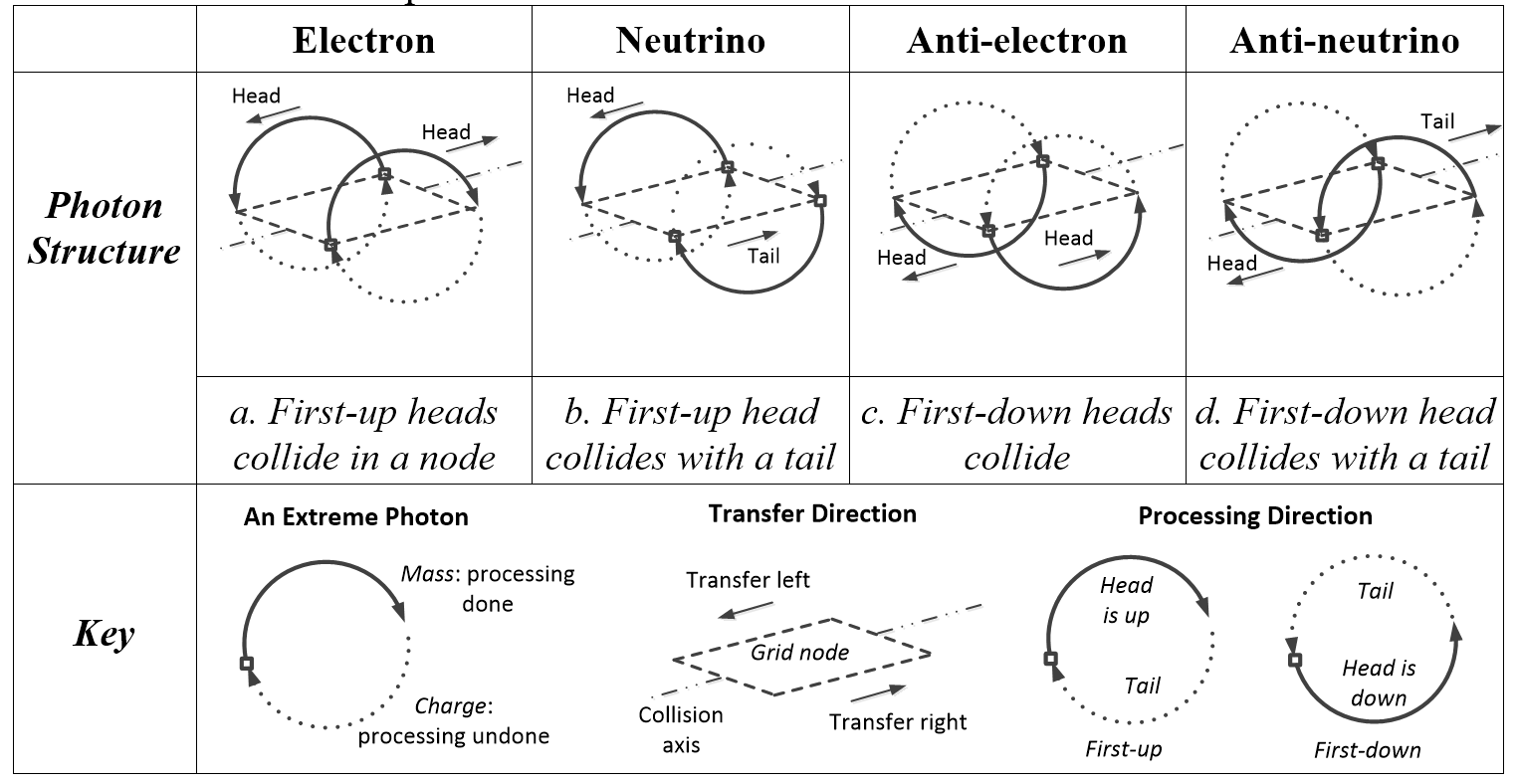
Figure 4.6 summarizes the leptons of physics by their photon structure as follows:
1. Matter. First-up extreme photons collide to give either an:
i. Electron (Figure 4.6a) First-up heads collide to give mass and a negative charge remainder.
ii. Neutrino (Figure 4.6b) First-up heads mostly cancel first-down tails to give a tiny mass but no charge remainder.
2. Anti-matter. First-down extreme photons collide to give either an:
i. Anti-electron (Figure 4.6c) First-down heads collide to give mass and a positive charge remainder.
ii. Anti-neutrino (Figure 4.6d) First-down heads mostly cancel first-down tails to give a tiny mass but no charge.
All the leptons of physics then have the structure of a one-dimensional photon collision.